https://github.com/shellphish/how2heap
how2heap을 따라 heap에 대한 공부에 입문하고자 한다.
glibc 버전 별로 크로스 컴파일을 해주기 때문에, 원하는 버전을 빠르고 쉽게 분석해볼 수 있다.
먼저, github에서 코드를 clone 받고, make를 통해 컴파일을 하자.
git clone https://github.com/shellphish/how2heap
cd how2heap && make
다음과 같이 파일이 구성된다.

공부 순서는 github README.md 파일에 있는 파일 순서대로 분석할 예정이다.

first_fit.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
fprintf(stderr, "This file doesn't demonstrate an attack, but shows the nature of glibc's allocator.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "glibc uses a first-fit algorithm to select a free chunk.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "If a chunk is free and large enough, malloc will select this chunk.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "This can be exploited in a use-after-free situation.\n");
fprintf(stderr, "Allocating 2 buffers. They can be large, don't have to be fastbin.\n");
char* a = malloc(0x512);
char* b = malloc(0x256);
char* c;
fprintf(stderr, "1st malloc(0x512): %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "2nd malloc(0x256): %p\n", b);
fprintf(stderr, "we could continue mallocing here...\n");
fprintf(stderr, "now let's put a string at a that we can read later \"this is A!\"\n");
strcpy(a, "this is A!");
fprintf(stderr, "first allocation %p points to %s\n", a, a);
fprintf(stderr, "Freeing the first one...\n");
free(a);
fprintf(stderr, "We don't need to free anything again. As long as we allocate smaller than 0x512, it will end up at %p\n", a);
fprintf(stderr, "So, let's allocate 0x500 bytes\n");
c = malloc(0x500);
fprintf(stderr, "3rd malloc(0x500): %p\n", c);
fprintf(stderr, "And put a different string here, \"this is C!\"\n");
strcpy(c, "this is C!");
fprintf(stderr, "3rd allocation %p points to %s\n", c, c);
fprintf(stderr, "first allocation %p points to %s\n", a, a);
fprintf(stderr, "If we reuse the first allocation, it now holds the data from the third allocation.\n");
}first_fit.c의 코드이다. 설명도 함께 fprintf로 출력해주는 것을 볼 수 있다.
먼저, glibc는 first-fit(최초 적합) 알고리즘을 사용한다. 따라서, free된 chunk가 있고 크기가 충분하다면 재할당 시 이 chunk를 사용하게 된다. 이 경우 use-after-free가 발생한다.
위 코드에서 a포인터 변수에 할당된 chunk를 free 후, c포인터 변수에 재 할당했을 시, a와 c포인터가 같은 chunk를 가리키고 있는 것을 보여주는 코드이다.
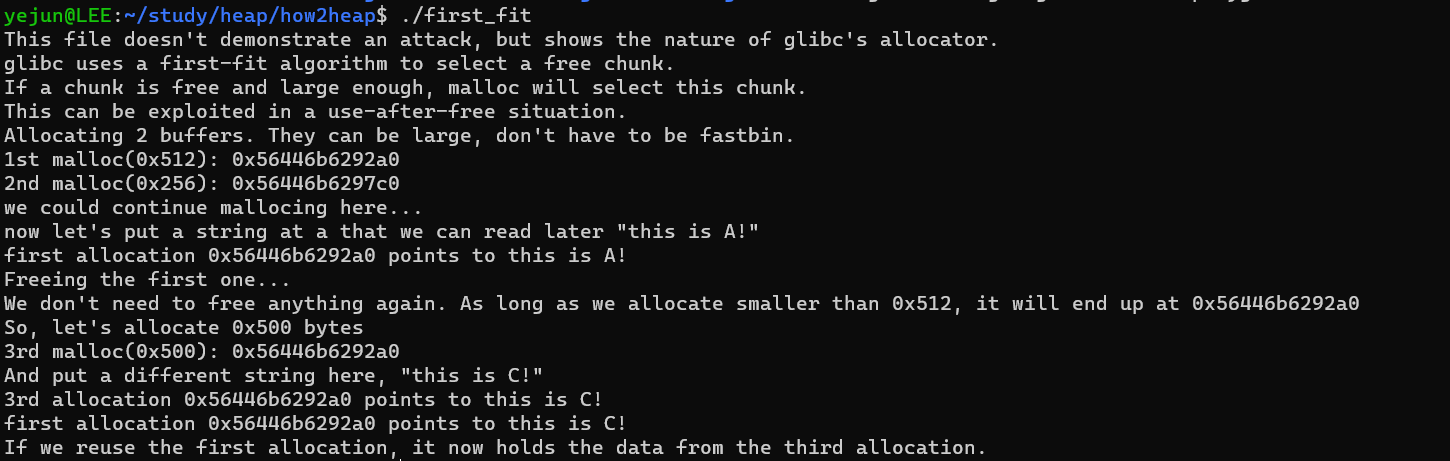
컴파일된 바이너리를 실행해보면, 코드에서 할당된 첫번째 할당된 a포인터 변수과 마지막에 할당된 c포인터 변수가 가리키는 chunk가 동일하여, 같은 데이터를 출력하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이는 기존에 할당된 포인터로 재할당된 데이터를 할당할 수 있는 것이며, UAF(Use-After-Free) Attack으로 활용될 수 있다.
Uploaded by N2T